(updated 4/26/2009, 5:00 p.m. w/clarification on the role of cost-benefit analysis in the regulation of greenhouse gases by the EPA)
“No amount of experimentation can ever prove climate models right; a single experiment can prove climate models wrong.”
– adapted from Albert Einstein quote.
Two days ago, on April 17, the EPA ruled that greenhouse gases (especially carbon dioxide) endanger human health and welfare. There is now a 60 day public comment period for people to give their opinions on this ruling before the EPA takes the next step and actually implements regulations on greenhouse gas emissions.
To help out, I’ve whipped up some commonly asked questions and their answers (below) on global warming to help you better understand the issues involved. As you will see, the science of global warming is far from ‘settled’. It is only because of the political and financial ramifications of global warming that so many people (mainly politicians and those who have vested interests) are trying to convince you otherwise.
IS GLOBAL WARMING HAPPENING NOW?
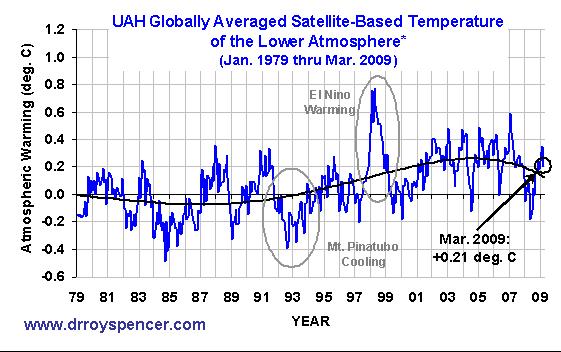
There is no way to know if warming is ‘happening now’. Because natural climate fluctuations on a year-to-year basis are so large, we will only recognize warming (or cooling) several years down the road when it appears in the rearview mirror. The most important statistic to me is that global average temperatures stopped rising in 2001, as shown in the following chart of global tropospheric temperatures that John Christy and I derive from satellite measurements.
As you can see, we might have even entered a new cooling trend. The claim that the warming trend over the last 50 to 100 years is continuing right now, or that it is even ‘accelerating’ is pure speculation, based upon the assumption that what has happened in recent decades will continue into the future.
ISN’T IT WARMER NOW THAN IT HAS BEEN IN THOUSANDS OF YEARS?
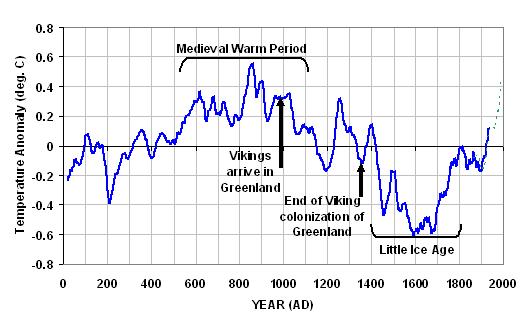
Well, look at the following recently published proxy reconstruction of global temperatures over the last 2000 years. This graph is based upon 18 previously published temperature proxies, and so provides the most robust estimate available to date. It can be seen that significant warming and cooling periods of 50 to 100 years in duration seem to be the rule, rather than the exception. There were probably even warmer years during the Medieval Warm Period (MWP) than we have seen in recent years. Even the warmth of the ‘record’ warm El Nino year in 1998 (see temperature chart above) might well have been surpassed several times during major El Nino events that occurred during the MWP. Unfortunately, there is no way to know how warm individual years were a thousand years ago…the graph below is made up of thirty-year averages. I added the dotted line toward the end showing the modern thermometer record.
ISN’T DISAPPEARING SEA ICE IN THE ARCTIC PROOF OF MANMADE GLOBAL WARMING?
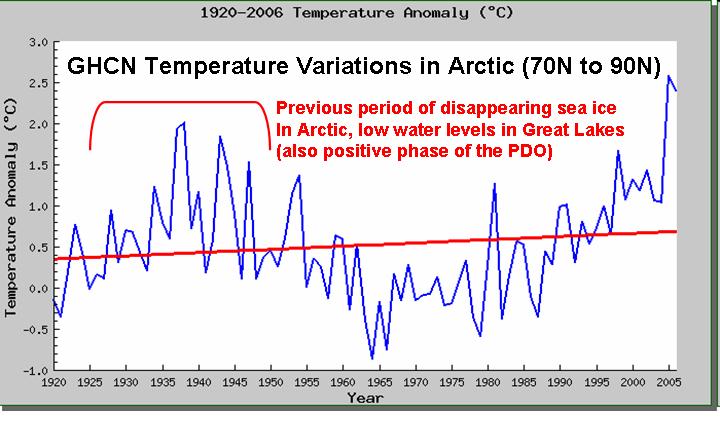
Warming, yes. Manmade, no. As can be seen in the following chart, it was just as warm in the Arctic (or nearly as warm) in the 1930s, with loss of sea ice and changing wildlife patterns reported in newspapers. The water levels in the Great Lakes reached record lows during this time, too…just as has happened again in recent years.
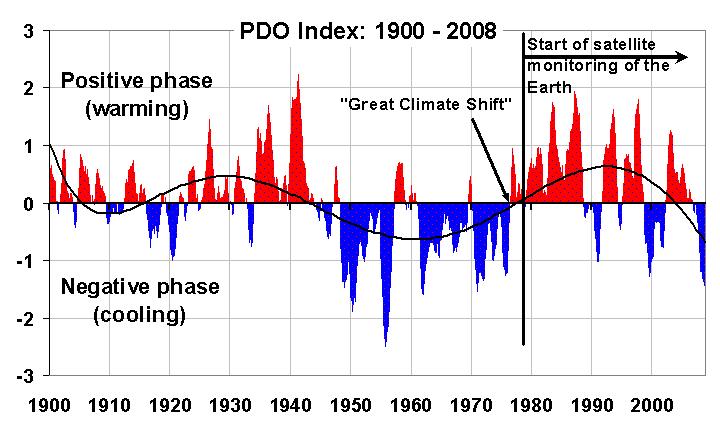
It should be remembered that we have had accurate satellite measurements of sea ice only since 1979, a period which has been entirely during the positive (warming) phase of the Pacific Decadal Oscillation (PDO, see graph below). The PDO is an index of weather patterns over the North Pacific Ocean that flips every 30 years or so. The coincidence that the satellite era started right after the “Great Climate Shift of 1977” has probably biased what we consider to be ‘normal’ for global climate. In fact, based upon the 2,000-year temperature graph shown previously, one might argue that there is no such thing as ‘normal’ climate.
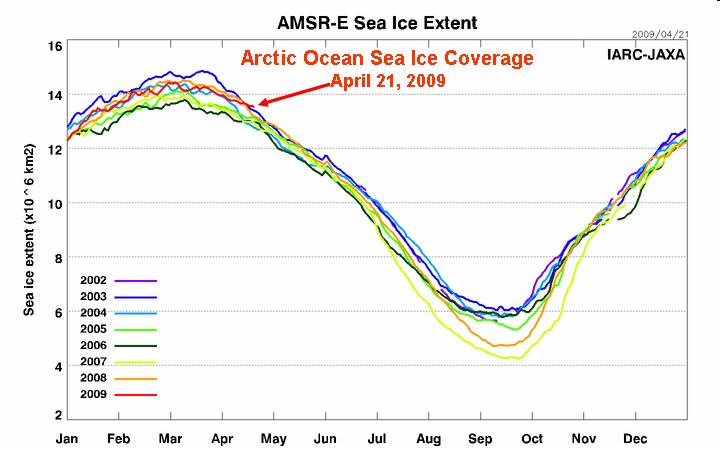
ISN’T ARCTIC SEA CONTINUING TO MELT FASTER AND FASTER?
No. As can be seen in the graph below (updated here through April 21, 2009), 2007 was the year when summer ice melt resulted in a 30-year record low in sea ice coverage. In 2008, the ice recovered somewhat. And from looking at 2009, we might well see further recovery this summer. Based upon the PDO index (above) it could be we have entered a new cooling phase of the PDO, which might explain this sea ice recovery, as well as our recent return to colder, snowier winters in the Northern Hemisphere.
AREN’T THE POLAR BEARS DYING FROM DISAPPEARING SEA ICE?
Generally speaking, no. While 2 sub-populations of polar bears appear to be threatened by the recent reduction in Arctic sea ice, the other dozen or more sub-populations are either stable or growing. Polar bears survived previous periods of Arctic warmth, and they will survive this one, too.
Polar bears, especially the cubs, tug at our heartstrings because they are so cute, and so make wonderful ‘poster children’ for global warming. What is ironic is that the polar bear is the only predator that will actively track down and eat a human being. The following two photos were sent to me by someone in Alaska…a polar bear that was waiting for a man to return to his truck.


You can learn the truth about the polar bear issue from a polar bear researcher here.
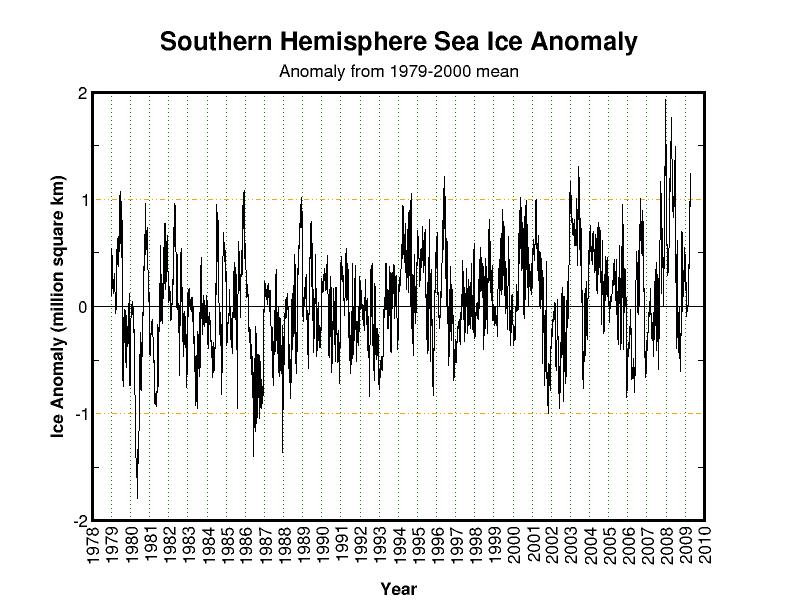
WHAT ABOUT THE COLLAPSING ICE SHELVES IN ANTARCTICA?
Just as Greenland glaciers will continue to flow downhill and break off into the sea as snow keeps falling on Greenland, the Antarctic ice sheet also slowly flows toward the sea. But in Antarctica, this forms ice ‘shelves’ that can extend out over the ocean a considerable distance. These ice shelves ring the entire continent, and eventually they must break off and float away. It could be that ice shelf collapse events become more common when warmer ocean waters affect a portion of the continent, as has been the case in recent years. Maybe a period of more rapid ice shelf collapse also occurred during the Medieval Warm Period of 1,000 years ago…we just don’t know.
On a whole, Antarctica has not warmed. And because it is so cold there, even a few degrees of warming will not cause the ice sheet to melt anyway. In fact, as can be seen in the following graph, sea ice around Antarctica has increased over the same 30-year period of time that Arctic sea ice has decreased.
ISN’T CARBON DIOXIDE A DANGEROUS GAS?
Well if you breathe pure CO2, you will die — from a lack of oxygen, not because CO2 is poisonous. But if you breathe pure oxygen for very long, that will also kill you. Carbon dioxide is necessary for life on Earth; photosynthesis by plants on land and by plankton in the ocean depend upon it. And without those forms of life, all the animals (and we humans) would die as well. For something as essential as CO2, it verges on the bizarre for people like Al Gore to liken carbon dioxide to sewage.
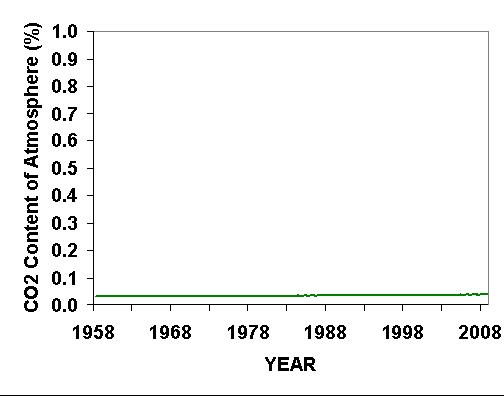
BUT WE CAN’T KEEP PUMPING CO2 INTO THE ATMOSPHERE FOREVER, CAN WE?
No…and we won’t. But the amount of CO2 we put into the atmosphere is pretty trivial: As of 2009, there are only 38 or 39 molecules of CO2 for every 100,000 molecules of atmosphere, and it will take mankind’s CO2 emissions another five years to raise that total by 1 molecule, to 40 out of every 100,000 molecules. The following graph shows how much the CO2 content of the atmosphere has risen in the last 50 years at Mauna Loa, Hawaii. The graph has a vertical scale that only extends to 1% of the atmosphere, and as can be seen, the increase in CO2 is barely visible. This graph is not a trick…it looks different from what you are used to seeing because CO2 is usually plotted with a greatly magnified vertical scale to make the CO2 rise look more dramatic. Yes, we might double the CO2 concentration of the atmosphere by late in this century…but 2 times a very small number is still a very small number.
ISN’T CO2 THE ATMOSPHERE’S MAIN GREENHOUSE GAS?
No. Water vapor accounts for about 85% or 90% of the Earth’s natural greenhouse effect, clouds account for another 5% or 10%. CO2 represents only about 3%, methane even less. You will see quite a bit of variability in the above percentages because they can only be calculated based upon theory, and involve a variety of assumptions. I have greatest confidence in the 3% number for the CO2 portion, which we have verified with our own calculations: The direct effect of doubling of CO2 would only be a 1 deg. C warming of the surface (this is not disputed, see below), and when you compare that to the 33 deg. C of surface warming due to all greenhouse components of the atmosphere, you get 3%.
BUT DON’T THE COMPUTER CLIMATE MODELS PREDICT SERIOUS GLOBAL WARMING…EVEN FROM THE LITTLE BIT OF EXTRA CO2 IN THE ATMOSPHERE?
Yes, but most of the warming produced by climate models is NOT directly from the CO2, but from assumed changes in clouds and water vapor in response to the small CO2-induced warming tendency. And this is the models’ Achilles heel. While all of those models now change clouds with warming in ways that amplify that warming, some by a catastrophic amount, there is increasing evidence that clouds in the real climate system behave in just the opposite way (peer reviewed papers of ours here and here). This could result in a doubling of atmospheric CO2 causing less than 1 deg. F of warming by the end of this century.
BUT WE’VE ALREADY SEEN 1 DEGREE OF WARMING…SO, WHAT COULD HAVE CAUSED IT?
My latest research (as yet unpublished) suggests most of the warming we’ve experienced in the last 100 years is due to natural changes in cloud cover…possibly caused by the Pacific Decadal Oscillation mentioned above. Something climate modelers apparently don’t appreciate is that it would only take about a 1% change in global cloud cover to cause ‘global warming’. Curiously, climate modelers do not believe this happens. Exactly why they don’t, I haven’t been able to figure out. Probably because we’ve not had accurate enough long-term observations of global cloud cover to document any such changes. But just because such changes are too small for us to measure doesn’t mean they do not exist. Most of us who were trained as meteorologists find 1% changes in global cloud cover to be entirely plausible, probably the result of natural, chaotic changes in weather patterns coupled to small chaotic changes in ocean circulation.
HASN’T THE “FINGERPRINT” OF MANMADE WARMING ALREADY BEEN FOUND?
No. Climate modelers claim they can only explain global warming by including greenhouse gas increases in their models. But that claim is based upon 2 critical assumptions: (1) the climate system is very sensitive to increasing CO2, a consequence of their climate models not handling clouds properly, and (2) as mentioned above, a lack of accurate observations over a long enough period of time to document potential natural, and stronger, warming mechanisms…such as a slight decrease in global cloud cover letting more sunlight in.
Another “fingerprint” claim is that global warming has been stronger over land than ocean, as would be expected with more greenhouse gases. But warming of the oceans and land in response to fewer clouds would be indistinguishable from warming caused by more carbon dioxide. A decrease in oceanic cloudiness would warm the oceans, which would then send more humid airmasses over land. And since water vapor is our main greenhouse gas, the land will warm in response. The land warming would be then be stronger than the ocean warming because the heat capacity of land is less than that of the ocean. So, don’t be fooled when you hear claims that the “fingerprint” of manmade warming has been found…it hasn’t. In fact, there is no known human “fingerprint”.
HAVEN’T SEVERE WEATHER EVENTS LIKE HURRICANES BECOME MORE COMMON IN RECENT YEARS?
No, only storm damage has increased. This is because people keep building along coastlines and in other areas prone to severe weather. And the more stuff we build, the more targets there are for hurricanes and tornadoes to destroy. Some of the records you have heard about for strongest hurricane, etc., are mostly because our technological ability to measure these storms has improved so much in recent years. There is no way to know if some recent storms (e.g. Katrina when it was in the central Gulf of Mexico) were stronger than major hurricanes that occurred in the early 20th Century, before we had weather radar, high resolution satellite data, and instrumented planes to fly into them.
WHAT ABOUT OCEAN ACIDIFICATION FROM MORE CO2?
The chemistry of the ocean is still poorly understood from the standpoint of how it varies over time, and how it is controlled. There is a common view among oceanographers that extra atmospheric CO2 has caused the average pH of the ocean to be reduced from 8.18 to 8.10 since the start of the Industrial Revolution. But pH varies widely across the global oceans, and that estimated decrease is more of a ‘theoretically-calculated expectation’ than it is an actual observation. A minority view I have heard is that the buffering capacity of the ocean will prevent ocean acidification. In fact, recent evidence suggests that (just like plants on land) plankton in the ocean will grow faster and be more abundant with more CO2 in the atmosphere.
AREN’T SPECIES GOING EXTINCT EVERY DAY DUE TO GLOBAL WARMING?
Generally speaking, there is no way to know if any species are going extinct. We would have to inventory all of the life that exists on every acre of the Earth to determine this, and as it is, science is discovering new species all the time. And, as discussed above, even if warming is causing some species to become extinct, that warming is likely to be mostly natural anyway. As is the case with climate models, statistics about species extinctions are largely theoretical calculations, based upon dubious assumptions. And in science, it is always the long-held assumptions that end up misleading us.
SHOULDN’T WE BE GETTING OFF FOSSIL FUELS ANYWAY, NO MATTER WHAT THE SCIENCE SAYS?
We eventually will…but right now there are no energy technologies that can offer replacements on the massive scale of what humanity needs for energy on a daily basis. Solar, wind, biofuels, only nibble around the edges of the problem, and they bring their own disadvantages (e.g. environmental impacts of wind and solar, rising food prices from diverting corn production from food to fuel). Both government (using your tax dollars) and private industry (using part of the money you spend on goods and services) have been researching new energy technologies for decades. The free market is the best way to solve this problem because, whoever develops new cost-effective energy technologies stands to make a fortune.
You can not simply legislate new sources of energy into existence. And if you try, economies will be hurt – if not decimated. The world’s poor, those living on the edge of the economy, will be the first to suffer. Since energy is required for everything we do, an increase in energy prices translates directly into more expensive goods and services across the economy.
And given the global nature of trade and business, misguided energy policies at home will simply drive many companies to other countries…where they can pollute even more than they used to here in the U.S..
SOME FINAL REMARKS ABOUT SCIENCE
There is a time-honored tradition in science that has led to a general public distrust of scientists: extrapolation into the future. Even in the 1800’s this failing of science was recognized:
“There is something fascinating about science. One gets such wholesale returns of conjecture from such a trifling investment of fact.”
-Mark Twain, Life on the Mississippi (1883)
As an example, consider the record low water level in Lake Superior experienced in 1926, shown in the graph below:
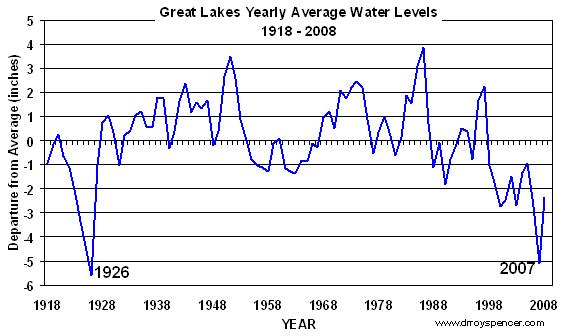
Here is what an ‘expert’ from that time said about the record-low lake levels (try not to laugh too hard):
“Ultimate extinction of the American side of the falls at Niagara is mathematically certain unless water levels in the Great Lakes are raised.”
-Daily Mining Journal, May 27, 1926.
Now, that wild statement was probably true in a literal sense. Note that it coveyed a maximum amount of alarm without being factually false. And this is exactly the same kind of prose contained in the Policymakers Summary of the latest (2007) report from U.N. Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC), a document that purposely minimizes any scientific uncertainties about anthropogenic global warming, while at the same time maximizing alarm.
Ultimately, fears of manmade global warming, species extinction, and ocean acidification arise from scientists not fully understanding the checks and balances which exist in nature. Nature is not static, but causes its own, internally-generated changes – both in climate and in biological systems. The common view that nature is in some sort of “delicate” balance is a romantic or religious opinion, and it is a view even held by most scientists. But balances in nature are always readjusting, either to internal forces or external forces. Nature is dynamic, not static. Just because a state of balance might be observed at any point in history does not mean that balance is in any way “delicate”.
Why is it OK for the presence of trees on Earth to change ecosystems and the climate system, but not for the presence of humans? Yes, nature must adjust to the presence of humans, but animals and plants are always adjusting to the presence of other animals and plants, anyway. Conferring these rights to plants and animals, but not to ourselves, makes absolutely no sense.
And since there is abundant scientific evidence that nature prefers more CO2 in the atmosphere, we need to seriously consider the possibility that burning of fossil fuels is, on balance, a good thing for life on Earth.
THE EPA IS ABOUT TO CAUSE A REGULATORY TRAIN WRECK
The US Chamber of Commerce has just issued a concise statement of the consequences of the EPA’s endangerment ruling, and it is a good introduction to the policy implications of the ruling.
I am told by those in the know that, if the EPA’s endangerment finding stands, it can then be used to justify any action to control energy policy and economic activity. While the section of the Clean Air Act that is involved in this has in the past also addressed cost/benefit analysis, it appears that regulating greenhouse gas emissions will not involve cost-benefit analysis. The endangerment finding instead discusses a ‘precautionary’ approach, where the indirect and uncertain effects of the U.S. sources of greenhouse gases on climate are recognized, but are ignored in an effort to help the climate change situation, no matter how small or incremental that help might be.
New regulations on CO2 emissions for new cars and trucks based on the endangerment finding will follow quickly. Numerous lawsuits to apply those auto regulations to other sections in the Clean Air Act will spread like wildfire. Many of these lawsuits are already in the system.
Folks, this is nothing like fixing the stratospheric ozone problem by developing other refrigerants to replace Freon. CO2 is produced by nearly all sources of energy. CO2 is a part of nature; Freon was a manmade chemical. While replacements for Freon were already developed by the time Freon was banned, we have no large-scale replacements for fossil fuels we can switch to in the near future.
This issue is at least as important as our recent global financial crisis – probably more so in the long run. It has been said that regulating carbon dioxide emissions will make the United States the cleanest Third World country on Earth. And whoever controls carbon dioxide emissions will control the world.
Finally, you can expect that the threat of the EPA regulating CO2 will cause many politicians and pundits to advocate congressional cap-and-trade legislation as a more palatable alternative. But the choice will be like deciding whether you want to die quickly or slowly. Either one will be lethal.
Instructions for Submitting Comments to the EPA

 Home/Blog
Home/Blog



