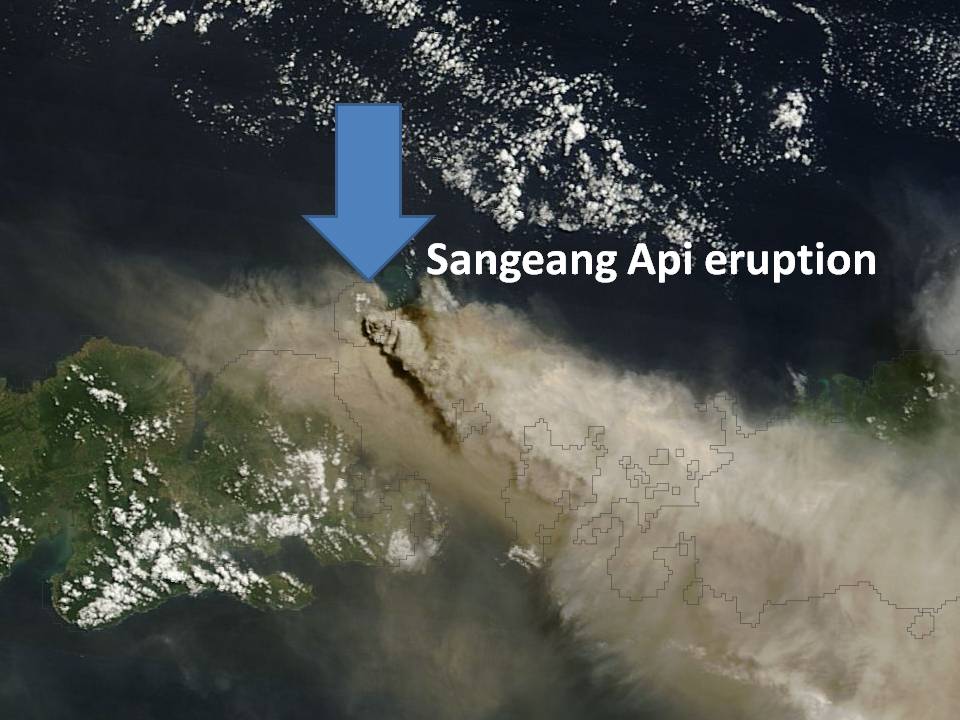
Yesterday’s eruption of the Sangeang Api volcano in the Sundra Islands produced an ash cloud which appears to have reached the stratosphere, a necessary (but not sufficient) condition for it to temporarily cool the climate system.
A NASA MODIS satellite image of the eruption shows the ash cloud drifting southeastward toward Australia, where all flights from Darwin have been grounded:
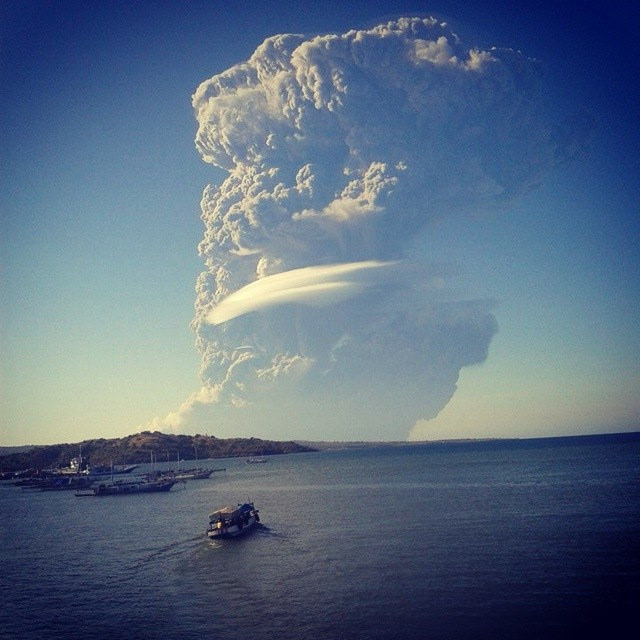
Details of the eruption can be found here. This backlit photo shows the anvil-type structure which supports the view that the plume has reached the lower stratosphere (Photo credit Courtney Robba, Dunia Baru):

Here’s another spectacular photo:

I have not yet seen any estimates of the sulfur output from the eruption, which is what will determine its potential to reduce incoming sunlight and cause cooling. I suspect it will be nowhere near the Pinatubo eruption of 15 June 1991, which produced 20 million tons of SO2.

 Home/Blog
Home/Blog