Weather.com published an article noting that the two Cat 4 hurricane strikes this year (Harvey and Irma) is a new record. Here’s a nice graphic they used showing both storms at landfall.

Left: Hurricane Harvey makes landfall near Rockport, Texas, on Aug. 25, 2017 | Right: Hurricane Irma makes its first landfall at Cudjoe Key, Florida, on Sept. 10, 2017 (graphic: Weather.com).
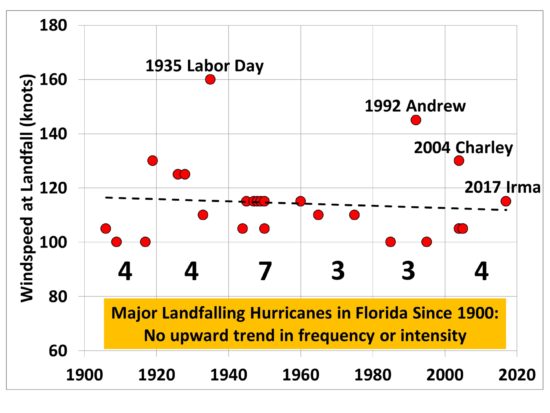
But the statistics of rare events (like hurricanes) are not very well behaved. Let’s look at this new record, and compared it to the 11+year period of no major hurricane strikes that ended when Harvey struck Texas.
The Probability of Two Cat 4 Strikes in One Year
By my count, we have had 24 Cat 4 or Cat 5 landfalls in the U.S. between 1851 and 2016. This gives a probability (prior to Harvey and Irma) of one Cat4+ strike every 7 years. It also leads to an average return period of two Cat4+ strikes of about 50 years (maybe one of you statiticians out there can correct me if I’m wrong).
So, since the average return period is once every 50 years, we were overdue for two Cat4+ strikes in the same year over the entire 166 period of record. (Again, for rare events, the statistics aren’t very well behaved.)
The Probability of the 11-Year “Drought” in Major Landfalling Hurricane
In 2015, a NASA study was published which calculated how unlikely the (then) 9-year stretch with no major hurricane landfalls was. They came up with a 177 year return period for such an event.
I used that statistic to estimate what eventually happened, which was 11 years with no major hurricane strikes.
I get a return period of 560 years!
Now, which seems more unusual and potentially due to climate change: something that should happen only once every 50 years, or every 560 years?
Maybe global warming causes fewer landfalling major hurricanes.

 Home/Blog
Home/Blog