It is no secret that I doubt increasing CO2 in the atmosphere will have enough negative effects on the global environment to warrant the extreme cost to humanity of substantially reducing those effects. Note that this statement has both science and energy policy components. In fact, with “global greening” we should consider the possibility of net positive benefits.
The public perception of global warming risks has involved a mixture of exaggerated claims regarding both the science and the energy policy, instigated by a minority of activist scientists and amplified by an eager news media. In my Kindle e-book Global Warming Skepticism for Busy People, I list 5 questions I believe must be answered in the affirmative before embarking on any large-scale decarbonization of the global economy:
The Five Big Questions
1) Is warming and associated climate change mostly human-caused?
2) Is the human-caused portion of warming and associated climate change large enough to be damaging?
3) Do the climate models we use for proposed energy policies accurately predict climate change?
4) Would the proposed policy changes substantially reduce climate change and resulting damage?
5) Would the policy changes do more good than harm to humanity?
As I state in my book, it is not obvious that the answer to any of the five questions is yes, let alone all of them. The first three questions deal with the science, and the last two deal with energy policy.
Regarding the first question, I might concede it is indeed possible most of the warming since the 1950s is human-caused. This is a core conclusion of the IPCCs 5th Assessment Report (AR5).
But so what? What it acknowledges is rather unremarkable, given (as we will see) the rather slow rate of global warming. As the second question asks, is the human component large enough to cause substantial damage? There has yet to be any good evidence produced that weather extremes are worse in recent decades than in previous centuries. Even warming itself appears to have begun in centuries past, before humans could be blamed, with proxy evidence of previous receding glaciers and low Arctic sea ice extent (and very high extent during the Little Ice Age) begging the questions of just how large natural climate variations have been, and what is the naturally preferred state of the climate system anyway?
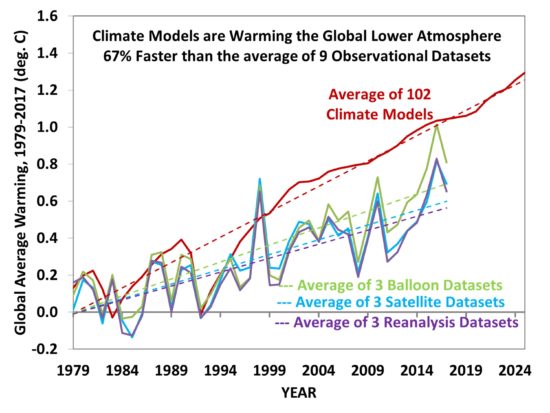
This leads to the third question, which has to do with the fact the latest generation of climate models produce, on average, about 2 times too much warming compared to the rates at which the global surface temperature and deep ocean have observed to have been warming, with the latest energy budget study (which makes the same climate forcing assumptions over the last 100+ years as the models) suggesting more like 1.6 deg. C of eventual warming from a doubling of atmospheric CO2, rather than 3.2 deg. C projected by the average climate model. (And even THAT assumes ALL of the warming is human-caused!)
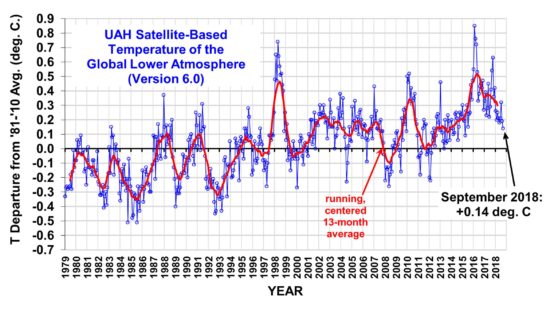
In the last 40 years, the discrepancy between models and observations for the globally-averaged lower atmosphere looks like this:
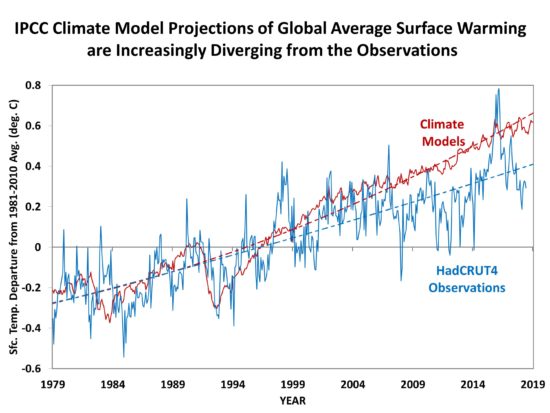
The discrepancy in the surface temperatures is less dramatic, but growing:
How can such models, which are increasingly portrayed as accurate, be defended with a straight face for energy policy decisions? The amount of warming they produce is not based upon physical first principles, as is often claimed. That some warming should occur is based upon fairly solid principles, but the amount of warming from increasing CO2 is entirely debatable.
The dirty little secret is that the models are tuned so that only increasing CO2 causes warming, since the various uncertain sources of natural climate change are either not known well enough to include, or are purposely programmed out of the models. (How do I know? Because NONE of the natural energy flows in and out of the climate system are known to the accuracy [about 1%] needed to blame recent warming on increasing CO2, rather than on Mother Nature. Those natural energy flows in the models are simply forced to be in balance, and so the cause of model warming ends up being anthropogenic. Thus the models use circular reasoning to establish human causation.)
The fourth and fifth questions have to do with whether we can really reduce CO2 emissions as long as humanity needs fossil fuels to reduce poverty and create prosperity. I have nothing against alternative energy sources per se, as long as they are practical and cost-competitive. Everything humanity does requires energy, and as long as China and India continue to reduce poverty with ever-growing usage of fossil fuels, global CO2 emissions will continue to increase, no matter what the United States does. With about 1 billion people in the world still without electricity, I believe it is immoral to deprive them of access to affordable energy.
Out of the 5 Big Questions, which are most important? Ultimately, economics is what rules peoples lives. Poverty kills, and forcing people to use more expensive energy will worsen poverty.
In France we are seeing the violent push-back against green energy policies (among other , mainly economic, issues), and we havent even yet reached the point where policies will reduce future CO2 emissions by enough to measure the effect by the end of this century in terms of global temperature. So, if you think the Paris riots are bad, wait until you see the public response to policies that will reduce future CO2 emissions by, say, 50%.
But we cannot ignore the science. What if the science was absolutely certain we were in for 20 deg. C of warming and a collapse of the Antarctic ice sheet, with 200 ft. of sea level rise? Then humanity might be willing to make large sacrifices to save itself. So, the science does matter… the question is, can it be trusted?
Based upon the observed rate of global warming (which is too small for any individual to feel in their lifetime), and failed climate model projections, I’d say the current state of the science is not yet ready for primetime.
For now, the science supports some modest and mostly harmless warming, but not enough warming to justify CO2 emissions reductions that would destroy the global economy, worsen global poverty, and have no measureable effect on global temperatures by the end of this century anyway.

 Home/Blog
Home/Blog