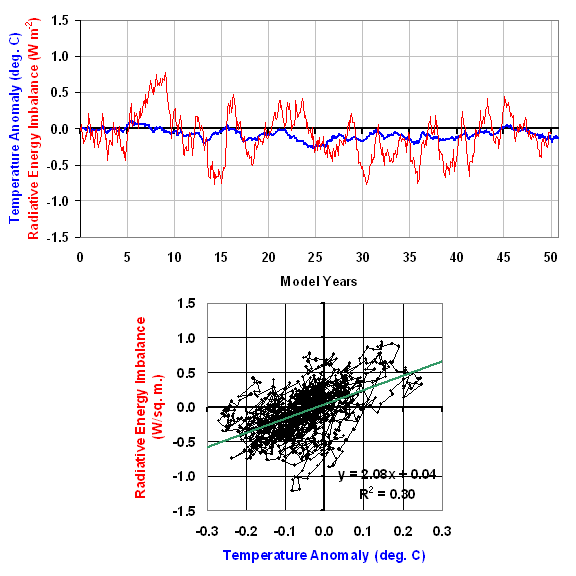
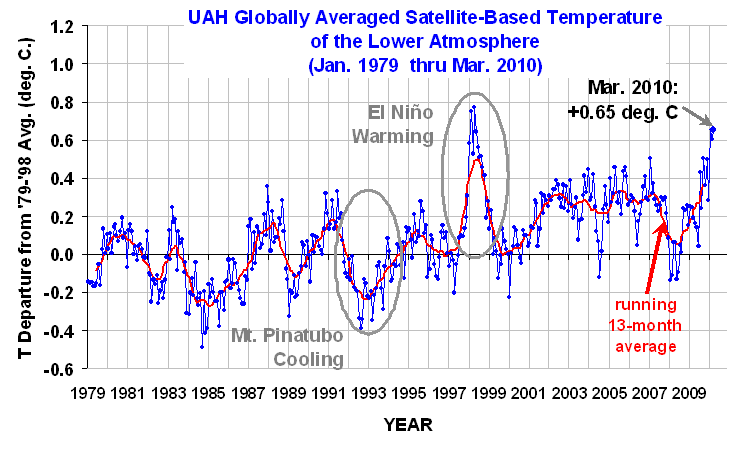
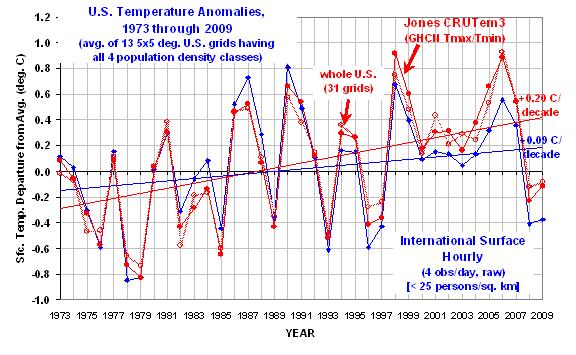
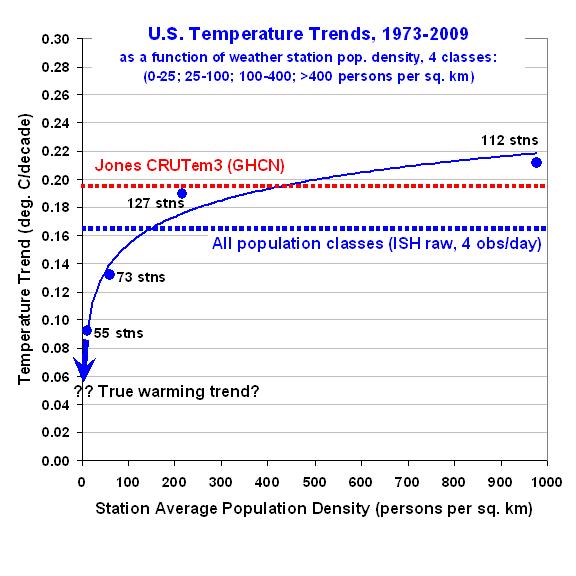
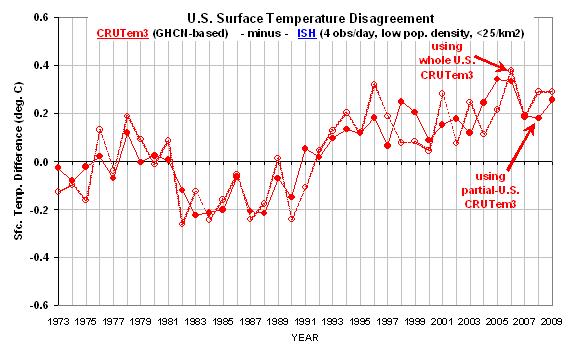
I have always been intrigued by solar power. Getting free energy from the sun is an attractive idea — if one ignores the fact that the equipment necessary to convert that “free” energy into a useful form can get a little pricey.
So, combining my interest in solar power with my wife’s desire that our swimming pool warm up faster in the spring (and stay warm later in the fall), I had an excuse to finally build a solar heater for our swimming pool.
Now, I could have bought one of the many products on the market for doing this, but what fun would that be? I wanted to build something from scratch, something that would help start conversation when people visit.
And if it actually worked, that would be even better.
And now, after about 6 hours and $260 invested, I have a portable system that is producing “free” solar energy and dumping it into the pool. Yes, I know I could have built it cheaper…but that wasn’t my goal.
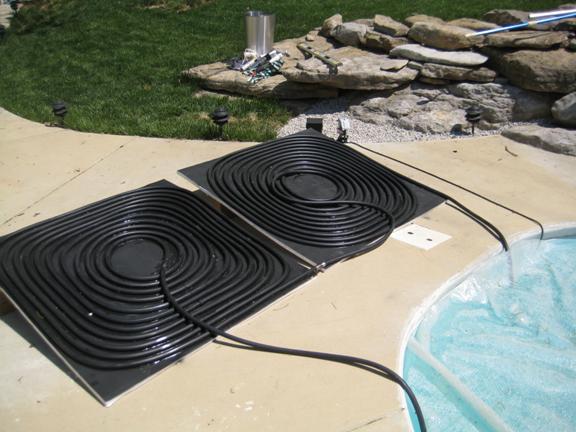

I started with the observation that our garden hoses get really hot when sitting in the sun. So, I thought, why not use black garden hoses as the solar collector? I then computed how much area is covered by a 100 foot garden hose…not very much…just over 6 sq. ft. Since I wanted to go with expensive “eco”-rated lead-free rubber hoses, I didn’t want to have to buy too many of those puppies.
So, since I knew that commercial solar collectors had water tubes embedded in black, solar-absorbent sheets of metal (which is where most of the solar energy is absorbed), I decided I would attach the rubber hose to a homemade collector. The collector surface would then transmit that extra solar energy to the water hoses.
I started with a 4×8 foot sheet of Styrofoam insulation board, about 1 inch thick, to keep the collector lightweight and reduce heat losses through the back of the collector surface. I cut the 4×8 sheet in half, so I could make two separate 4×4 foot collectors, permitting easier carrying and storage when not in use.
For the collector surface I bought a 50 foot roll, 20 inches wide, of aluminum flashing used for roofing applications. I cut 4 foot lengths and glued down 3 of them to each Styrofoam sheet with construction adhesive. Aluminum has a very high thermal conductivity, about 9,000 times that of air, which is what you want for a solar collector. You want your materials to conduct most of the heat to the water circulating through the tubes before the surrounding air has a chance of stealing it away.
Now that I had 2 aluminum-covered Styrofoam sheets, the next step was to spray paint them black. Black is always the best solar absorber color…that’s why it’s black! Black reflects virtually no sunlight, and any sunlight that is not reflected from a solid, opaque surface must then be absorbed…which is what you want in a solar collector.
I used 1 can of flat black enamel spray paint for each of the two 4×4 foot collector surfaces. By the time the paint was dry, it was late enough in the morning for the sun to start peeking over the trees behind our house and start warming the collector surfaces. I put my hand on one — OUCH! Too hot to touch!…I thought to myself, “this is a good thing”.
The next step was to lay out 100 feet of black rubber garden hose on each sheet in a uniform spiral pattern, which then results in about 2 inches of collector surface separating each coil. Rubber has a thermal conductivity about 6 times that of air, so it is nowhere near as good a solar collector material as aluminum or copper. Copper tubing would have been a much better choice, with a thermal conductivity over 15,000 times that of air – but it would have also been much more expensive.
Next I needed to attach the hoses to the painted aluminum in such a way that the hot aluminum would efficiently transmit heat to the cooler water-filled hose. I had read somewhere that common silicone caulk has about 10 times the thermal conductivity of air, so my plan was to attach the hoses to the collector surfaces with black caulk.
But first I needed to get the garden hose to stay coiled in place, so I used a hot glue gun to tack it down. I quickly found that the hot collector surface and black hose sitting in the sun was too hot for the hot glue to solidify! How am I going to get around this problem?
I decided I would cool the hose by starting to pump pool water through it before the collectors were finished. I attached the $40 submersible fountain pump I bought at Lowes to one end of the hose, lowered it to the bottom of the pool, then draped the other end of the hose over the edge of the pool for the return flow. I plugged the pump in and, Voila!, my solar collection system was working before it was even assembled!
I proceeded to tack the hose down into position with the hot glue gun, which was a pain since hot glue does not stick to cool rubber worth a darn. I then used about 4 tubes of black silicone caulk on each of the collectors to seal both sides of the hose where it met the aluminum surface. This was the most tedious part of the job, with almost 400 feet caulk applied to almost 200 feet of hose.
As seen in the above photo, I made the collectors so they could be attached in series. That way, I could construct and add as many collectors as I wanted to the system.
After everything was hooked up and running, I checked to see how fast my 35 Watt pump was pumping water through the hose – I measured about 2 gallons per minute, which is 120 gallons per hour (gph). This is much less than the pump’s rating of 300 to 500 gph, but that’s due to the large amount of friction within 200 feet of garden hose.
The above picture was taken at 11:45 a.m. (1 hour before solar noon) on April 14, 2010. At that time, the two collectors together were raising the water temperature from 77 deg. F at the pump inlet to 85 deg. F at the outlet, a temperature increase of 8 degrees. So, every 60 seconds, the collectors together were warming 2 gallons of water by 8 deg. F. When you run the numbers, this ends up being an energy transfer rate of about 2.3 kilowatts.
Since the area of each of the two collectors is about 1.5 sq. meters, this means about 800 Watts per sq. meter of heat flux was being usefully generated by the collectors. I’m guestimating that this would be about 80% efficiency, assuming about 1,000 Watts per sq. meter is falling on my collectors at this time. (The sun’s elevation in the sky was approaching 65 degrees at this time, and I had the collectors tilted toward the sun at about 15 degrees.) By the way, none of the numbers I have come up are here meant to be very accurate.
Due to shading by trees, our pool gets only about 5 ˝ hours of direct sunlight each day, between 11 a.m. and 4:30 p.m., with solar noon occurring at 12:45 p.m. Since the elevation of the sun in the sky changes during that time, let’s assume I get the equivalent of 4 hours of solar energy at the rate mentioned above, measured at 11:45 a.m.
Our pool is a rather small fiberglass one, holding 6,600 gallons of water. I compute from the above numbers that the solar collection system adds about an extra 0.7 deg. F of warming on a sunny day, which is a 30% enhancement to the 2 deg. F of warming the pool experiences naturally on a sunny day.
What would it cost to heat the same amount of water with electricity? If I can get 2.3 kilowatts of heat input for 4 hours, that’s 9.2 kilowatt-hours of energy, which at our electric rate of about 9 cents per kwh, is only 83 cents worth of electricity per sunny day.
Hmmm.
For my investment of $260, at a daily savings of 83 cents, I will need to operate the solar collectors for 310 days (!) to reduce the cost per kilowatt-hour to that which I could have gotten from an electric pool heater. If we use the system for 30 sunny days in the spring, and then 30 sunny days in the fall (which seems unlikely), that would take about 5 years. Of course, an electric pool heater would also have cost something to buy, too.
So, maybe this project did not make much sense economically. But, looking on the bright side, what I gain from my investment is (1) a longer swimming season, (2) a conversation starter, and (3) an extra blog posting.

 Home/Blog
Home/Blog