The COVID-19 disease spread is causing a worldwide shutdown in economic activity as business close, airlines cancel flights, and people shelter in their homes. For example, there was a 28% decline in global commercial air traffic in March 2020 compared to March of last year.
Last month I described a simple method for removing the large seasonal cycle from the Mauna Loa CO2 data, and well as the average effects from El Nino and La Nina (the removal is noisy and imperfect), in an effort to capture the underlying trend in CO2 and so provide a baseline to compare future months’ measurements too.
What we are looking for is any evidence of a decline in the atmospheric CO2 content that would be strong enough to attribute to the economic downturn. As can be seen, the latest CO2 data show a slight downturn, but it’s not yet out of the ordinary compare to previous month-to-month downturns.
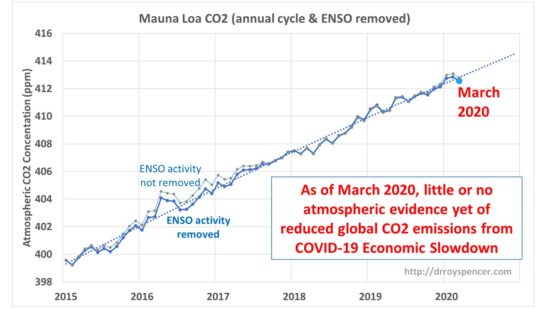
I personally doubt we will see a clear COVID-19 effect in the CO2 data in the coming months, but I would be glad to be proved wrong. As I mentioned last month, those who view the economic downturn as an opportunity to reduce atmospheric CO2 would have to wait many years — even decades — before we would see the impact of a large economic downturn on global temperatures, which would occur at great cost to humanity, especially the poor.

 Home/Blog
Home/Blog



